Physicists Explain How Human Eyes Can Detect Quantum Effects
September 30, 2009 | Source: PhysOrg.com
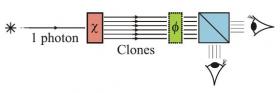
How human eyes could detect quantum entanglement: A single-photon qubit is amplified through cloning via stimulated emission in a nonlinear crystal (red box). The clones are split into two orthogonal polarization modes, with the polarization basis varied with the help of a wave plate (green box). Each mode is then detected by a naked human eye. (Pavel Sekatski, et al.)
Below a certain threshold number of incoming photons, the eye remains blind (no light is seen), whereas above the threshold, the probability of seeing) is close to one.
