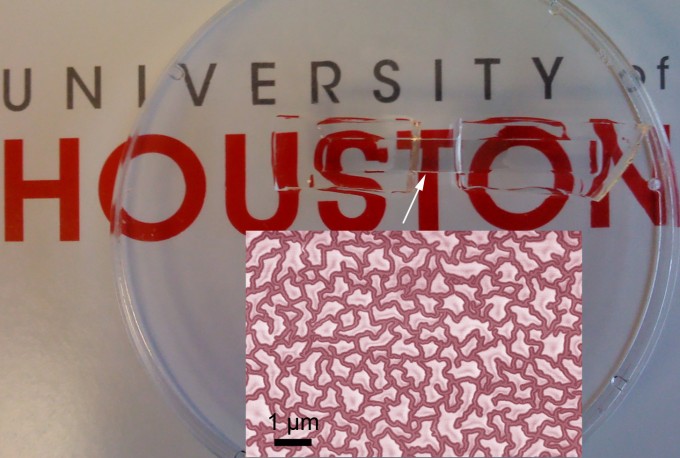
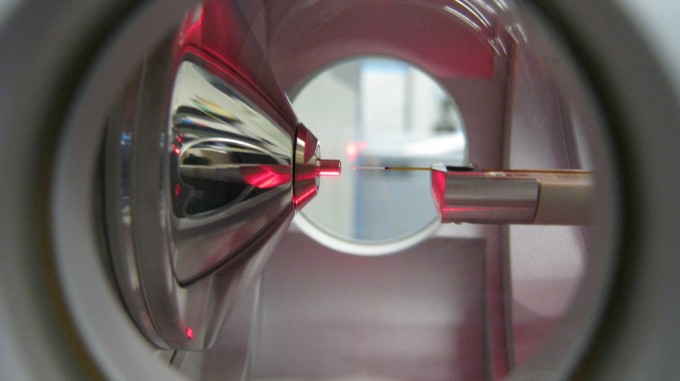
X-ray imaging protein molecules at atomic resolution using a graphene cage
New imaging method could provide new insights into illness at the molecular level
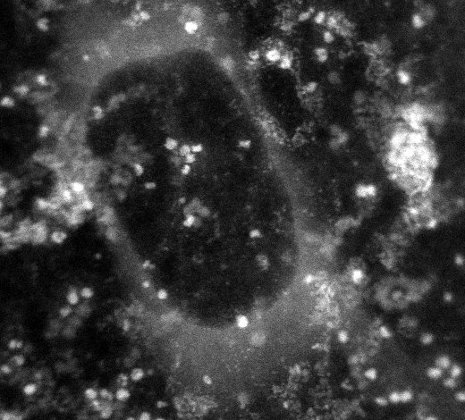
Nanoparticle pinpoints blood-vessel plaques
A step toward identifying plaques vulnerable to rupture that causes heart attack and stroke
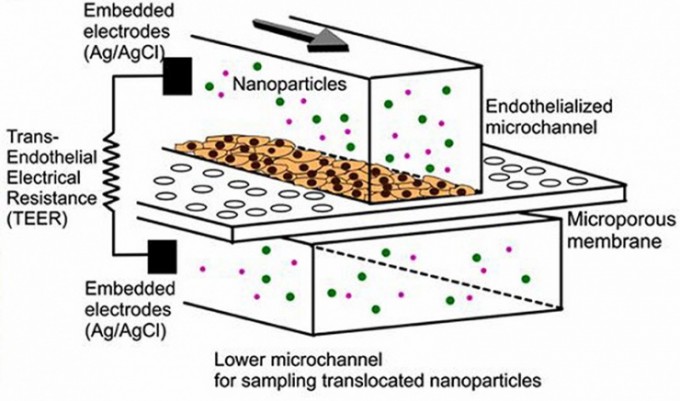
Mimicking atherosclerosis with blood cells on a microchip
Speeding up nanomedicine research by bypassing the 15-year FDA process for nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems
New form of graphene allows electrons to behave like photons
Could lead to ultra-fast graphene-based computing devices and superconductivity
The first flexible, transparent, and conductive material
Could finally lead to a fully foldable cell phone or television screen